New Piranha Species Discovery in Bolivia Highlights Biodiversity Research
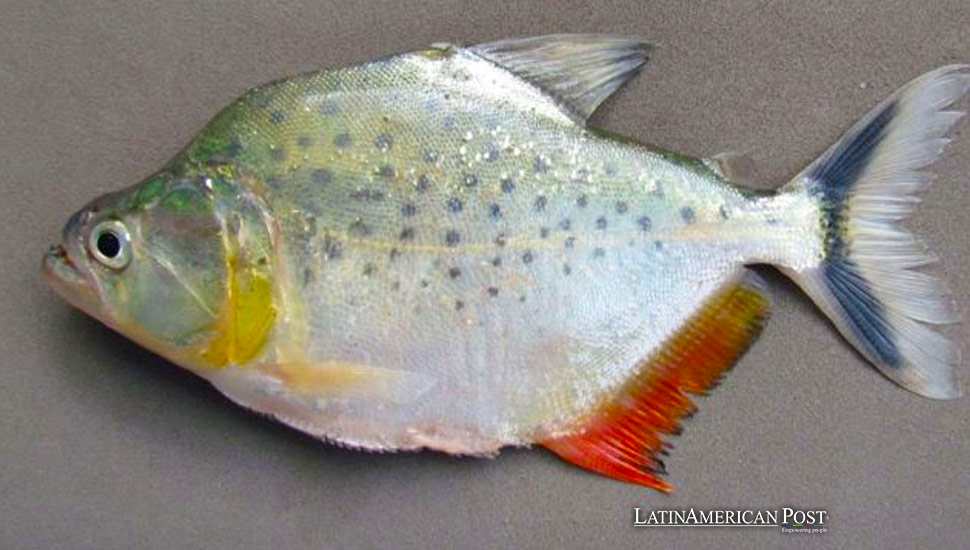

A team of biologists has discovered a new piranha species, Serrasalmus magallanesi, in Bolivia’s Madeira River, underscoring the importance of studying the Amazon Basin’s fish fauna to understand better and conserve its rich biodiversity.
A team of biologists has made a groundbreaking discovery in the Amazon Basin-a new species of piranha, Serrasalmus magallanesi, found in the Madeira River of Bolivia. This remarkable find not only underscores the critical importance of researching the ichthyofauna of the Amazon Basin but also piques our curiosity about the rich biodiversity of this region and the potential for further discoveries.
Technology in Biodiversity Research
The discovery of Serrasalmus magallanesi involved sophisticated technological tools and methodologies. The team, led by the University Mayor of San Simón in Cochabamba, Bolivia, and supported by the Autonomous University of Madrid, meticulously analyzed 159 individuals from eight known species and the potential new species of Serrasalmus in Bolivia.
The biologists utilized various technologies to identify and describe the new species accurately. They conducted 33 morphological measurements and 17 morphological counts, including scale counts, fin rays, and teeth. Additionally, they analyzed ten coloration variables and employed radiography to examine vertebrae, ribs, and fin rays, measuring specific bones to distinguish Serrasalmus magallanesi from other species.
Genetic analysis played a crucial role in confirming the species’ uniqueness. The researchers could establish genetic differences between Serrasalmus magallanesi and other closely related species by comparing DNA sequences. This combination of morphological and genetic data provided a robust framework for formally identifying and describing the new piranha.
The Role of Advanced Techniques in Discovering New Species
The application of advanced techniques such as radiography and genetic analysis in biodiversity research is a testament to the evolving nature of this field. Historically, many species were identified based on visual and morphological characteristics alone, leading to misidentifications and gaps in our understanding of biodiversity. However, the integration of modern technologies has revolutionized this field, providing us with more precise and accurate species identification methods.
For instance, radiography allows scientists to examine the internal structures of fish, such as bone arrangements and fin supports, which are often critical in distinguishing closely related species. This non-invasive technique provides detailed insights without harming the specimens, making it a valuable tool in biodiversity research.
Genetic analysis, on the other hand, offers a molecular approach to species identification. By comparing genetic markers, researchers can detect subtle differences between species that may not be apparent through morphological examination alone. This method is beneficial in regions like the Amazon Basin, where high biodiversity and cryptic species (morphologically similar but genetically distinct) pose significant challenges to traditional taxonomic methods.
Implications for Conservation and Future Research
The discovery of Serrasalmus magallanesi has profound implications for conservation efforts in the Amazon Basin. Understanding the biodiversity of this region is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. Each new species discovery contributes to a more comprehensive picture of the ecosystem, allowing scientists and policymakers to identify priority areas for protection and monitor the health of fish populations more accurately.
The Amazon Basin is a biodiversity hotspot, home to many species that remain undiscovered. However, it is also a region under threat from human activities such as deforestation, mining, and illegal fishing. These activities can devastate the ecosystem, leading to habitat loss, pollution, and declines in species populations.
Researchers can provide valuable data supporting conservation initiatives by documenting and studying new species like Serrasalmus magallanesi. For example, a newly discovered species in a particular area might highlight the need to protect that habitat from destructive activities. Additionally, understanding the ecological roles of different species can help manage fish populations sustainably and ensure the entire ecosystem’s health.
Regional and Global Significance
The discovery of Serrasalmus magallanesi adds to the growing body of knowledge about South America’s biodiversity, particularly in regions like Bolivia that are less studied compared to other parts of the Amazon Basin. This find is the ninth piranha species discovered in Bolivia and the 32nd in South America, underscoring the region’s rich and largely unexplored biodiversity.
The findings also emphasize the importance of international collaboration in biodiversity research. The joint efforts of Bolivian and Spanish researchers exemplify how global partnerships can enhance scientific understanding and contribute to conservation efforts. Such collaborations combine diverse expertise and resources, enabling more comprehensive and impactful research.
Moreover, the discovery of Serrasalmus magallanesi has broader implications for the scientific community and the public. It raises awareness about the richness of the Amazon’s biodiversity and the need to protect this invaluable natural heritage. Public engagement and education are crucial to conservation efforts, as they foster a sense of responsibility and stewardship towards the environment.
Future Directions in Biodiversity Research
The successful identification of Serrasalmus magallanesi sets the stage for further research in the Amazon Basin. Future studies will likely focus on understanding the ecology and behavior of this new species, its interactions with other species, and its role within the ecosystem. Such research can provide insights into the evolutionary processes that drive biodiversity in the Amazon and help identify factors that contribute to species resilience or vulnerability.
Advancements in technology will continue to play a pivotal role in biodiversity research. Emerging techniques such as environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis, which involves collecting DNA from ecological samples like water or soil, hold great promise for detecting and monitoring species in a non-invasive manner. This method can be particularly useful in remote or inaccessible areas, providing a powerful tool for discovering and studying biodiversity.
Also read: Bolivian Chefs Create the World’s Largest ‘Sándwich de Chola’
The discovery of Serrasalmus magallanesi in Bolivia’s Madeira River highlights the importance of technological advancements in biodiversity research. Radiography, genetic analysis, and other modern techniques have enabled a more precise understanding of species diversity and contributed to conservation efforts in the Amazon Basin. This discovery enriches our knowledge of the region’s biodiversity and underscores the need for continued research and international collaboration to protect and preserve the Amazon’s unique ecosystems.