Colombia Bolsters Firefighting Arsenal With Drug Crop Fumigation Planes Amid El Niño
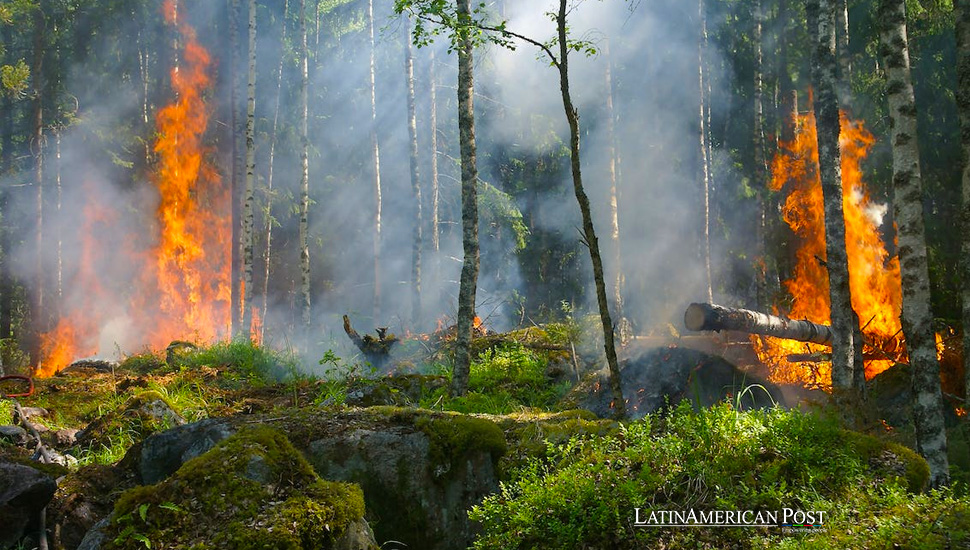
In response to devastating wildfires intensified by El Niño, Colombia has expanded its firefighting fleet with eight aircraft, including planes once used for drug crop fumigation. This move, part of a broader Latin American struggle against fires, underscores the region’s commitment to preserving its biodiversity.
A Proactive Approach to Wildfire Threats
Colombia, known for its lush landscapes and rich biodiversity, has recently taken significant steps to combat the increasing threat of wildfires, exacerbated by the dry conditions associated with the El Niño weather phenomenon. In a proactive move, the Colombian government, led by President Gustavo Petro, has augmented its firefighting capabilities by incorporating eight aircraft into its fleet. This strategic decision reflects a broader narrative of environmental stewardship and adaptation in the face of climatic adversities, a theme that resonates across Latin America.
Historically, Latin America has grappled with the dual challenges of natural disasters and human-induced environmental degradation. Colombia, the world’s second-most bio-diverse country, is no stranger to these trials. President Petro’s recent declaration of a natural disaster in January, in response to rampant wildfires, highlights the acute vulnerability of the nation’s ecosystems. This crisis is not isolated; it echoes across the continent, from the Amazonian rainforests to the Patagonian steppes, where fires have often raged uncontrollably, threatening biodiversity, livelihoods, and the global climate.
Adding four AT-802 Air Tractor planes and four Black Hawk UH-60 helicopters to Colombia’s firefighting arsenal is noteworthy for several reasons. These aircraft, notably repurposed from their previous roles in anti-narcotics operations, symbolize a shift in national priorities towards environmental conservation and disaster response. The AT-802 Air Tractors, known for their agility and payload capacity, alongside the robust and versatile Black Hawk helicopters, form a formidable force against the flames. This transition from combating illicit drug cultivation to fighting fires represents a significant reallocation of resources in pursuit of safeguarding natural heritage.
The use of these aircraft in drug crop fumigation operations, explicitly targeting coca plantations with the herbicide glyphosate, was halted in 2015 amid growing concerns over the chemical’s health impacts. This pivot from a controversial practice to a focus on environmental protection underscores a broader regional trend toward reevaluating and repurposing resources to address emergent ecological and climatic challenges.
Repurposing Resources for Environmental Safeguarding: Colombia’s Strategic Shift
Colombia’s initiative is set against a broader Latin American struggle with wildfires. Countries like Brazil, Argentina, and Chile have also faced severe fire seasons driven by dry weather, El Niño effects, and human activities such as deforestation and agricultural burning. The regional response has varied, with nations investing in firefighting resources, enhancing early warning systems, and implementing policies to mitigate climate change and its attendant risks.
The challenge of wildfires in Latin America is compounded by the region’s significant contribution to global biodiversity. As home to the Amazon rainforest, the Andes mountains, and vast savannas and wetlands, Latin America’s ecological health is paramount to the planet’s climate regulation, water cycles, and species diversity. The fires pose an immediate threat to this biodiversity and contribute to climate change by releasing carbon stored in forests and peatlands.
In addressing these fires, Latin American countries are protecting their natural and cultural heritage and contributing to global efforts to combat climate change. For example, the repurposing of aircraft in Colombia represents a small but significant step towards a more resilient and responsive environmental strategy that acknowledges the interconnectedness of local actions and global outcomes.
Lessons for a Resilient Future: Integrating Technology and Traditional Knowledge
As Colombia and its neighbors refine their approaches to wildfire management and environmental conservation, the lessons learned will be critical for other regions facing similar challenges. Integrating technology, such as satellite monitoring and advanced firefighting aircraft, with traditional knowledge and community engagement offers a holistic path forward. Moreover, the experience of repurposing resources for environmental protection provides a compelling narrative for countries worldwide grappling with the need to adapt to changing priorities in the face of climate change.
Also read: Mexican Armed Forces Uncover Largest Meth Lab Amid Uptick in Drug Trafficking
Colombia’s bolstering of its firefighting fleet amidst the threat of El Niño-induced wildfires is a testament to its commitment to preserving its environmental legacy. This action, reflective of a broader Latin American endeavor to combat the increasing prevalence of wildfires, underscores the urgent need for regional cooperation, innovative resource use, and a sustained commitment to the planet’s ecological well-being. As Latin America faces the flames, the world watches and learns, recognizing the intrinsic value of these biodiverse lands and the critical importance of protecting them for future generations.




